|
Nicole T. Liberati, Jonathan M. Urbach, Sachiko Miyata, Daniel Lee, Eliana Drenkard,
Gang Wu, Tao Wei, Jacinto M. Villanueva, Frederick M. Ausubel
|
|
|
| Overview |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram negative 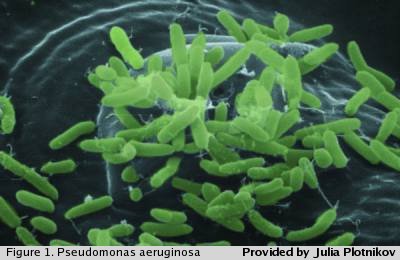 aerobic rod-shaped bacterium that is ubiquitous in the environment, living in the soil, in water and on plant and animal tissues. P. aeruginosa is also an opportunistic human pathogen, causing infections when normal immune
defenses are disrupted. Burn patients are commonly afflicted with P. aeruginosa infections. Respiratory P. aeruginosa infection is the leading reason for morbidity in cystic fibrosis patients.
aerobic rod-shaped bacterium that is ubiquitous in the environment, living in the soil, in water and on plant and animal tissues. P. aeruginosa is also an opportunistic human pathogen, causing infections when normal immune
defenses are disrupted. Burn patients are commonly afflicted with P. aeruginosa infections. Respiratory P. aeruginosa infection is the leading reason for morbidity in cystic fibrosis patients.
PA14 is a clinical isolate obtained from a burn patient that displays pathogenicity in a variety of
genetically tractable model hosts and mice (2
3
4
5
10).
To facilitate study of P. aeruginosa we have created an extensive library of PA14 transposon insertion mutants and
identified the transposon insertion site in each mutant(17).
From this library, we have selected mutants to be included in a
PA14 Non-Redundant Transposon Insertion Mutant Set (PA14NR Set). A single mutant for each successfully disrupted gene has been
colony-purified and included in the PA14NR Set. This ordered set of mutants is ideal for genome-scale screens.
|

